Introduction to SERP
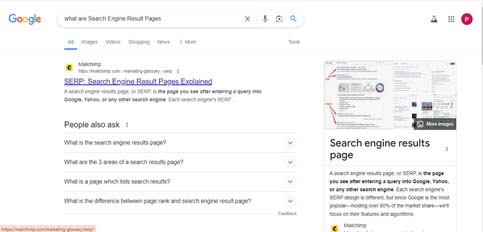
Before we start, it is important to know what are Search Engine Result Pages? Search Engine Result Pages (SERP) are the pages displayed by search engines like Google or Bing after you type in a query. They’re like digital maps guiding you to the most relevant websites based on your search.
Importance of SERP
SERPs are crucial for online visibility because they determine where your website appears when someone searches. Being on the first page can mean more visitors, while lower rankings may lead to fewer clicks. Think of it as a popularity contest where the higher you rank, the more attention you get.
Overview of Elements on SERP
On a SERP, you’ll see different sections like organic results, which are regular listings based on relevance to your search. Paid results are ads that businesses pay for to appear at the top. Featured snippets provide quick answers, while knowledge panels offer more detailed information. These elements shape your search experience, helping you find what you need faster.
What are the key components of SERP?
There are various components of SERP. So let’s get right into it.
The key components of a Search Engine Results Page (SERP) play a vital role in determining the visibility and success of a website. Let’s delve into each component in simpler terms:
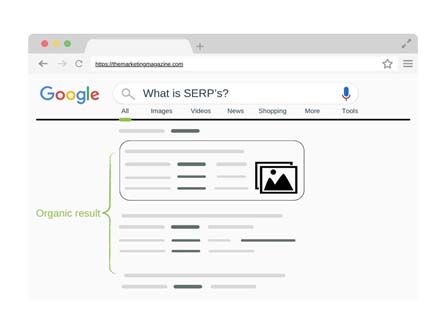
A. Organic Results
1. Description of Organic Listings: Organic results are the unpaid listings that appear on the SERP based on their relevance to the user’s search query. These listings are determined by the search engine’s algorithm.
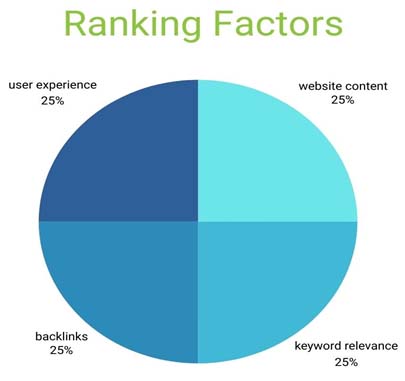
2. Ranking Factors: The ranking of organic results is influenced by various factors such as website content, keyword relevance, backlinks, and user experience. Websites that meet these criteria are more likely to appear higher in organic search results.
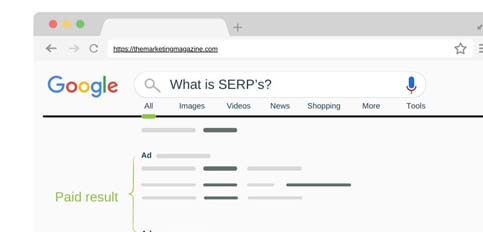
B. Paid Results
1. Explanation of Paid Listings: Paid results, also known as advertisements or sponsored listings, are placed on the SERP by advertisers who pay the search engine to display their ads. These listings are marked as ads and appear above or below organic results.
2. Ad Rank and Quality Score: Advertisements on the SERP are ranked based on factors like bid amount, ad quality, and relevance. Advertisers with higher ad ranks and quality scores are more likely to have their ads displayed prominently.
C. Featured Snippets
1. Definition and Purpose: Featured snippets are summaries of questions or doubts that have been asked by any user. They aim to provide users with quick and relevant information without requiring them to click on a specific search result.
2. Optimization Strategies: To optimise for featured snippets, website owners can structure their content in a way that directly answers common user questions or queries. This involves using clear headings, bullet points, and concise answers.
D. Knowledge Graph
1. Introduction to Knowledge Graph: The Knowledge Graph is a database of interconnected information collected by search engines to enhance search results with factual information. It aims to provide users with immediate answers to their queries.
2. Enhancing Information Displayed: Website owners can enhance the information displayed in the Knowledge Graph by ensuring their content is accurate, relevant, and structured in a way that search engines can easily understand. This may involve using schema markup to provide additional context to search engines.
Features of SERP
Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) are more than just a list of links nowadays. They’re dynamic, packed with features designed to give users quick and relevant answers. Here’s a breakdown of these SERP features, explained in simple language:
1. Organic Results: These are the traditional listings of web pages that appear in response to a search query. They’re ranked based on relevance to the user’s query and other factors like website authority and content quality.
2. Paid Results: These are advertisements that appear at the top or bottom of the SERP. They’re labelled as ads and are often targeted based on the user’s search query. Advertisers pay to have their listings displayed here.
3. Featured Snippets: These are highlighted boxes that provide direct answers to user queries at the top of the SERP. They aim to answer questions quickly without users needing to click through to a website.
4. Knowledge Graph: This is a box of information that appears on the right side of the SERP, providing quick facts and details about a topic. It pulls information from various sources to give users a snapshot of what they’re searching for.
5. Rich Snippets: These are enhanced search results that include additional information like reviews, ratings, and other metadata. They stand out visually and provide more context to users about the content of a webpage.
6. Local Pack: This feature displays a map and a list of local businesses related to the user’s search query. It’s especially useful for queries with local intent, like “restaurants near me” or “plumbers near me.”
7. Image and Video Carousels: These are horizontal scrolls of images or videos that appear at the top of the SERP. They provide visual content related to the user’s search query, making it easier to find multimedia content.
8. People Also Ask (PAA) Boxes: These are expandable boxes that appear in the SERP, displaying questions related to the user’s query. When clicked, they reveal more information and related questions, helping users explore further.
9. Site Links: These are additional links that appear below the main search result for certain websites. They provide quick access to specific sections or pages within a website, making navigation easier for users.
10. Reviews and Ratings: Some SERPs display ratings and reviews directly in the search results, particularly for businesses and products. This helps users make informed decisions without having to visit multiple websites.
These features make SERPs more user-friendly and informative, providing users with a variety of options to find the information they need quickly and easily.
Understanding SERP rankings
Search engine result page (SERP) rankings are influenced by a combination of factors, including search engine algorithms and user behaviour. Understanding these elements is crucial for improving website visibility and achieving higher rankings.
A. Search Engine Algorithms
1. Overview of Algorithmic Ranking:
Search engines like Google use complex algorithms to determine the order in which search results appear on SERPs. These algorithms analyse various factors to provide users with the most relevant and authoritative content for their queries.
2. Factors Influencing Rankings:
Several factors contribute to algorithmic ranking, including:
– Relevance: The extent to which a webpage matches the user’s search intent and query.
– Quality: The overall quality of the content, determined by factors like accuracy, credibility, and comprehensiveness.
– Authority: The authority of a webpage, determined by the number and quality of backlinks pointing to it.
– User Experience: Factors such as page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and overall usability contribute to a positive user experience, which can impact rankings.
B. User Behavior and Personalization
1. Impact of User Behavior on SERP:
User behaviour plays a significant role in determining SERP rankings. Search engines track metrics like click-through rate (CTR), bounce rate, and dwell time to gauge the relevance and usefulness of search results. Websites with higher engagement metrics are often rewarded with higher rankings.
– Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of users who click on a search result after seeing it on the SERP. A higher CTR indicates that the result is relevant and appealing to users.
– Bounce Rate: The percentage of users who navigate away from a website after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate may indicate that the content is not relevant or engaging to users.
– Dwell Time: The amount of time users spend on a web page after clicking on a search result. Longer dwell times signal that the content is valuable and engaging.
2. Personalized Search Results:
Search engines also personalise search results based on factors like the user’s search history, location, and device. Personalization aims to deliver more relevant and tailored results to individual users, enhancing the overall search experience.
– Search History: Search engines consider a user’s past search queries and interactions to customise future search results.
– Location: Location-based personalization ensures that users receive results relevant to their geographical location, such as local businesses or events.
– Device: Search engines may display different results based on the device used for the search, optimising for factors like screen size and browsing habits.
Some unique SEO strategies for SERP success
Here are some straightforward strategies to help you achieve this:
1. Keyword Research: Identify relevant keywords that your target audience is likely to search for. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner to find popular and less competitive keywords to target.
2. On-Page Optimization: Optimise your website’s on-page elements such as title tags, meta descriptions, headers, and content with your chosen keywords. Ensure that your content is well-structured, informative, and easy to read.
3. Quality Content: Create high-quality, engaging content that addresses the needs and interests of your target audience. Regularly update your website with fresh and valuable content to keep visitors engaged and encourage search engine crawlers to index your site more frequently.
4. Mobile Optimization: With more users accessing the internet on mobile devices, ensure that your website is mobile-friendly. Responsive design and fast loading times on mobile devices are essential for improving user experience and SERP rankings.
5. Backlink Building: Earn backlinks from reputable and relevant websites to improve your site’s authority and credibility in the eyes of search engines. Focus on building quality backlinks from sources that are relevant to your industry or niche.
6. Local SEO: If your business serves a specific geographic area, optimise your website for local search by creating and optimising Google My Business listings, obtaining local citations, and earning positive reviews from satisfied customers.
7. Social Media Presence: Maintain an active presence on social media platforms to engage with your audience and drive traffic to your website. Social signals such as likes, shares, and comments can indirectly impact your SERP rankings.
8. Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor your website’s performance using tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console. Track your keyword rankings, organic traffic, and user engagement metrics to identify areas for improvement and adjust your SEO strategy accordingly.
Analysing and monitoring SERP
SERP monitoring and analysis involves keeping an eye on how your website appears in search engine result pages (SERPs) and understanding the data to improve your online presence. By using tools like Google Search Console or third-party SEO software, you can track your website’s performance in search results over time.
Analyzing SERP data helps you identify trends, such as changes in rankings or traffic, and understand how your SEO efforts are paying off. It allows you to spot opportunities for improvement, such as optimizing content for specific keywords or addressing technical issues that may be impacting your visibility.
By regularly monitoring and analyzing SERP data, you can stay informed about your website’s performance, adapt your SEO strategy as needed, and ensure that you’re maximizing your chances of success in organic search results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the dynamics of SERP is crucial for online success. Understanding its components, optimizing for key features, and monitoring performance are essential strategies. By adapting SEO techniques to meet the evolving landscape of search engine result pages, businesses can enhance visibility, attract more traffic, and ultimately achieve their digital marketing goals.